Before we go down the memory lane, decode the Google Algorithm Odyssey and unravel their SEO impacts let us understand a few concepts.
- What is an algorithm?
- What does the Google Algorithm do?
- Why is the Google algorithm important?
- How often does Google update its algorithm?
What is an algorithm?
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure or a set of rules designed to solve a specific problem or perform a particular task. In the realm of computing and mathematics, algorithms serve as a sequence of instructions, typically used by computers to process data, perform calculations, and automate various tasks.
Fundamentally, algorithms are the backbone of computer science, guiding the way in which data is processed, analyzed, and transformed. They can range from simple, well-defined sequences of operations to complex, multi-layered procedures that deal with vast amounts of information.
The primary goal of an algorithm is to provide an efficient and effective way to solve a problem or execute a task, often by breaking it down into smaller, more manageable steps.
What does the Google Algorithm do?
The Google Algorithm refers to a complex system used by Google's search engine to determine the relevance, quality, and ranking of web pages in response to user queries.
Why is the Google algorithm important?
Its primary function is to sort through the massive amount of web content available and provide users with the most relevant and high-quality results based on their search queries.
The overarching goal is to provide users with the best possible answers to their search queries while combating spam, low-quality content, and manipulation.
How often does Google update its algorithm?
As the Google search results depend on the Google algorithm the algorithm is of core importance for every SEO. The very fact that there are minor updates on a regular basis the SEO industry has to keep a track and also be aware of the major updates.
The main goal of every update is to combat spam in any form to make search results more relevant for the user.
The major updates are announced by Google on their search blog and also shared on social media by Google. Understanding the impact of every update on the search results is what keeps every SEO on their toes.
As a company policy, Google does not comment on what their new updates do. There are no new guidelines on their site for webmasters or SEO community other than the same old narration of how ‘very good content’ would be rewarded and ‘unethical techniques’ would be penalized.
Algorithms are always closely guarded secrets of search engines since any leak would mean an abuse of the system leading to contamination of their search results. Silence pays. Any comment, acceptance or a denial on the new algorithm behavior usually lets out parts of the algorithm secret.
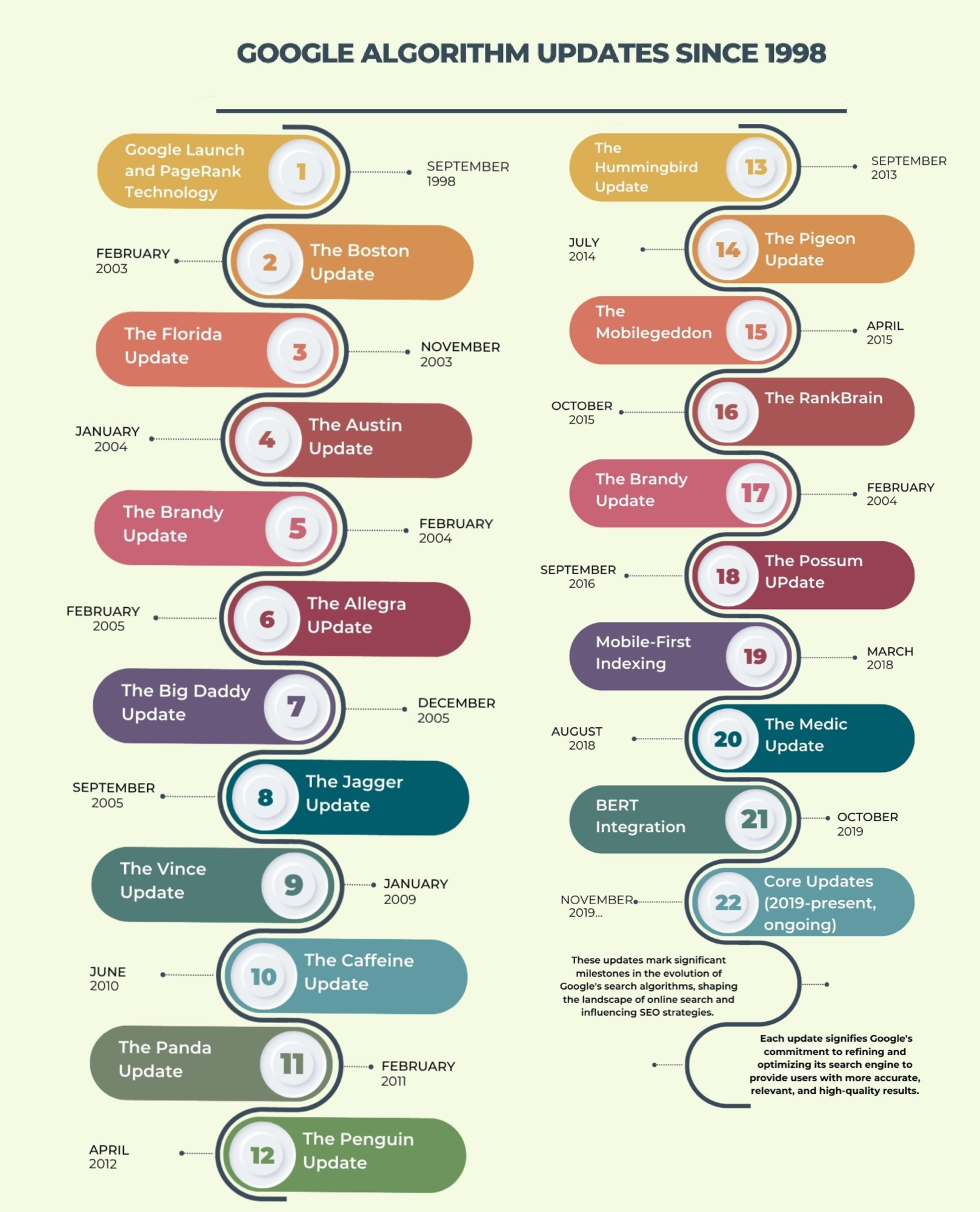
List of Major Google Algorithm Updates:
- Google Launch (1998): Birth of Google as a search engine with PageRank technology.
- Boston (2003): Focused on link quality and anchor text relevance.
- Florida (2003): Targeted keyword stuffing and manipulative SEO tactics.
- Austin (2004): Aimed to differentiate quality content from spam.
- Brandy (2004): Improved semantic search and relevance understanding.
- Allegra (2005): Emphasized trust factors, link quality, and duplicate content.
- Big Daddy (2005): Infrastructure update focusing on crawling and indexing.
- Jagger (2005): Addressed manipulative link building and low-quality backlinks.
- Vince (2009): Speculated to favor larger brands in search results.
- Caffeine (2010): Enhanced speed and indexation of websites.
- Panda (2011): Targeted thin, low-quality content and content farms.
- Penguin (2012): Focused on web spam, particularly manipulative link schemes.
- Hummingbird (2013): Emphasized understanding user intent and context in searches.
- Pigeon (2014): Focused on local search results and ties between local and core algorithms.
- Mobilegeddon (2015): Gave priority to mobile-friendly websites in mobile search results.
- RankBrain (2015): Introduced machine learning for understanding search queries better.
- Possum (2016): Enhanced the importance of the user's location in search results.
- Fred (2017): Targeted low-value content primarily existing for revenue generation.
- Mobile-First Indexing (2018): Google started using the mobile version of a site for ranking and indexing.
- Medic (2018): Primarily affected health and wellness sites, emphasizing expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (E-A-T).
- BERT (2019): Leveraged natural language processing for better understanding context in search queries.
- Core Updates (2019-present, ongoing): Regular broad updates focused on improving overall search quality.
Let us understand and delve deep into all the major Google Algorithm updates till date:
Google Launch (1998): The birth of Google as a search engine with the PageRank technology.
The inception of the Google saga can be traced back to 1995 at Stanford University. Larry Page, contemplating graduate school at Stanford, was guided around the campus by Sergey Brin, a fellow student.
Collaboratively, they crafted a search engine utilizing links to gauge the significance of individual pages across the World Wide Web. Originally dubbed "Backrub," this search engine underwent a transformation and emerged as "Google."
The nomenclature "Google" was a clever play on the mathematical term denoting 1 followed by 100 zeros, vividly encapsulating Larry and Sergey's mission to "organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful."
Distinguishing themselves from conventional search engines that relied on the frequency of search terms on a page, Larry and Sergey envisioned a more sophisticated system.
They conceptualized an algorithm called PageRank, which assessed a website's relevance based on the quantity of pages and the significance of those pages linked back to the original site.
This visionary approach marked a departure from the traditional methods of result ranking and laid the foundation for Google's transformative impact on information retrieval.
Boston (2003): Focused on link quality and anchor text relevance.
Following the integration of PageRank technology, Google underwent a pivotal algorithm update in February 2003. This update, complementing the significance of the number of links, introduced a crucial emphasis on the quality of links.
Distinguishing itself from previous iterations, this algorithm enhancement aimed at refining the relevance of search results. It achieved this by elevating the importance of various factors, including title tags and anchor text.
The Boston update played a pivotal role in not only improving the overall quality of search results but also setting the stage for subsequent updates that would further fine-tune and enhance Google's search algorithm.
Florida (2003): Targeted keyword stuffing and manipulative SEO tactics.
On November 16, 2003, Google implemented the Florida update, strategically timed just before the Christmas shopping season and the Pubcon Florida event in Orlando.
This update holds historical significance in the realm of search engine optimization (SEO) as it signaled a paradigm shift towards a more content-centric approach. The Florida Update emerged at a crucial juncture, aiming to address the prevalence of "keyword stuffing," a tactic that had become commonplace among black hat SEO practitioners following the Boston 2003 Update.
Central to the Florida Update was the objective of diminishing the effectiveness of such manipulative techniques. It specifically targeted spam practices like "cloaking," wherein different content is presented to search engines compared to users, and "doorway pages," pages designed solely for search engines, devoid of any value for users.
Marking the inaugural major Google algorithm update, the Florida update had far-reaching consequences, significantly impacting a substantial number of websites in what can be described as a catastrophic outcome.
Austin (2004): Aimed to differentiate quality content from spam.
Released in January 2004, the Austin update represented a significant overhaul of Google's search engine ranking algorithm. It directly followed the 2003 Florida update, which targeted spam sites relying on backlinks from link exchange farms. The Austin update aimed to further refine the search algorithm to combat manipulative tactics.
However, the update faced criticism from webmasters as unintended consequences ensued. Numerous websites not involved in the manipulative practices addressed by the update experienced substantial ranking losses. In response to feedback and identified issues, Google introduced the Brandy update, perceived as a corrective measure to rectify the shortcomings of its predecessor.
During this transition, noticeable shifts occurred in search results. E-commerce giants like Amazon and eBay frequently emerged as top hits, leveraging their extensive link networks. Another noteworthy change was the integration of dynamic web pages into the index, showcasing Google's commitment to adapting its algorithms to accommodate the ever-changing landscape of online content.
Brandy (2004): Improved semantic search and relevance understanding.
Released between late January and mid-February 2004, Google's Brandy update stands as the official successor to the Austin Update. Unlike altering the Google ranking algorithm, the Brandy Update focused on modifying the database or index, bringing about crucial improvements.
This update was particularly beneficial for numerous websites that had been unfairly penalized by deactivating certain evaluation criteria introduced by prior updates. The adjustments made during the Brandy update showcased Google's commitment to refining its processes and ensuring a fairer assessment of web content without fundamentally altering the underlying ranking algorithm.
Allegra (2005): Emphasized trust factors, link quality, and duplicate content.
Between February 2nd and 8th 2005, Google implemented the “Allegra Update,” marking a pivotal shift in its search algorithm. This update followed Google's extensive efforts to cleanse the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) from spam sites through previous updates like Florida, Austin, and Brandy in 2003-2004, setting the stage for a transformative moment in the SEO landscape.
The Allegra update of February 2005 was primarily geared towards Google's ongoing battle against spam websites. This conclusion is drawn from the observable results of the update, as the implementation of the algorithm change led to the exclusion of numerous spam sites from the SERPs.
Despite its impactful nature, Google has not officially disclosed details about the rollout of the Allegra update. Within the SEO community, there is no consensus on the specific aspects affected by the update. However, it is generally assumed that the algorithm adaptation targeted areas such as duplicate content, suspicious links, and latent semantic indexing, reflecting Google's commitment to refining search results by combating spammy practices.
Big Daddy (2005): Infrastructure update focusing on crawling and indexing.
The Big Daddy Google Algorithm Update of 2005 stands as a pivotal milestone in the evolution of Google's search engine. Crafted to bolster the search engine's prowess in comprehending and ranking web pages based on relevance and quality, this update instigated transformative changes.
Big Daddy ushered in significant modifications to Google's infrastructure, crawling mechanisms, and indexation processes. Its primary focus was on tackling issues like canonicalization, duplicate content, and URL handling. By emphasizing the importance of accuracy and reliability in search results, the update urged webmasters to produce high-quality, original content. Big Daddy laid a solid foundation for subsequent algorithm updates, embodying Google's ongoing commitment to refining its search engine capabilities.
Dubbed "Big Daddy," the nomenclature was deliberately chosen to distinguish it from other updates, imparting a distinctive and memorable identity. While speculation surrounds the name, it is widely believed that "Big Daddy" was selected to convey the update's significant and authoritative nature.
Undeniably a major update, Big Daddy left an indelible mark on search results and the practices of webmasters, highlighting its substantial impact on the evolving landscape of Google's search engine infrastructure.
Jagger (2005): Addressed manipulative link building and low-quality backlinks.
In September 2005, Google rolled out the Jagger update, the another significant algorithmic change in its history. Jagger marked a notable shift by placing a heightened emphasis on link quality, specifically penalizing websites associated with low-quality or spammy backlinks. Conversely, it rewarded sites boasting high-quality and authoritative backlinks, recognizing them as indicators of trustworthiness and credibility.
The crux of Jagger's impact lay in its targeting of low-quality links, encompassing paid links, link farms, and reciprocal links. By doing so, the update sought to refine the criteria for evaluating the quality of a website's link profile. This strategic move reflected Google's commitment to enhancing the overall quality of its search results by favoring websites with trustworthy and reputable link structures, thus promoting a more reliable and credible online environment.
Vince (2009): Speculated to have favored larger brands in search results.
The codenamed "Vince" represents a substantial and enduring modification to Google's ranking algorithm. Announced in 2009 and swiftly implemented globally, this algorithmic shift began to exert its influence on the German search market by December of the same year.
The Vince Update made its debut on January 18, 2009, bearing the name of a Google engineer as a tribute to his contributions to this significant algorithmic alteration. Matt Cutts, who led Google’s web spam team at the time, characterized it as a "simple change."
In essence, the Vince update constituted a rapid and conspicuous adjustment, particularly in terms of broad-level, competitive keyword terms. Its primary aim was to favor first-page rankings for prominent brand domains over sites that had previously occupied higher positions. This strategic alteration signaled a shift in Google's approach, reflecting an inclination toward recognizing and elevating the visibility of well-established and authoritative brands in the search results landscape.
Caffeine (2010): Enhanced the speed and indexation of websites.
On August 10, 2009, Google unveiled Caffeine, a pivotal update that would go on to be one of the most significant milestones in the history of the search engine.
The scale of the Caffeine Update was so immense that Google initiated a "Developer Preview" phase, spanning several months. Recognizing the critical nature of this update, Google granted SEO professionals and developers early access to identify and report any potential issues. Finally, on June 8, 2010, Caffeine was officially rolled out.
The primary objective behind Google Caffeine was to revolutionize the indexing process, enabling the web to be cataloged at a faster pace. This transformation aimed to provide users with more up-to-date and fresh content in search results, underscoring the increasing importance of speed and currency in the evolving landscape of the web.
The Google Caffeine infrastructure not only facilitated quicker indexing of the web but also ensured that the relevant data generated was presented to users in a format that aligned with their search queries.
This advancement marked a momentous shift in the dynamics of online search, ushering in an era where speed and the availability of fresh content became paramount considerations for an enhanced user experience.
Panda (2011): Targeted thin, low-quality content and content farms.
Google Panda made its debut in February 2011, as part of Google's concerted effort to eradicate black hat SEO tactics and web spam.
In the initial announcement on February 24, 2011, Google detailed the objectives of Panda Update 1.0 , emphasizing its intent to diminish rankings for low-quality sites.
These were defined as sites that added minimal value for users, copied content from other websites, or were deemed generally unhelpful. Simultaneously, the update aimed to elevate the rankings of high-quality sites, those featuring original content, research, in-depth reports, and thoughtful analysis.
Expressing enthusiasm for this ranking improvement, Google underscored its belief that Panda represented a substantial stride toward enhancing result quality. On April 11, 2011, Google transformed Panda into a global update, highlighting that adherence to Google's quality guidelines was crucial for site improvement.
In subsequent updates during May and June 2011, Google refined and optimized the algorithm for more efficient application. The focus was on rewarding sites that followed guidelines, enriched their content with quality, and served as valuable information sources for users.
Interestingly, when the Google Panda update initially launched, Google had not assigned an official name. Search Engine Land dubbed it the "Farmer" update, but Google later officially adopted the name "Panda" after a few days.
This update marked a significant milestone in Google's commitment to delivering higher-quality search results and combating content that failed to meet their quality standards.
For further details, you can visit: WebPro - Understanding and Adapting to the Google Panda Update
Penguin (2012): Focused on web spam, particularly manipulative link schemes.
In 2012, Google introduced the "web spam algorithm update," a strategic move aimed at combatting link spam and manipulative link-building practices.
This web spam algorithm eventually became officially known as the Penguin algorithm update. The nomenclature was revealed in a tweet by Matt Cutts, who served as the head of the Google web spam team at that time.
The Penguin Update served as the latest countermeasure integrated into the search algorithm to devalue sites employing manipulative tactics and spammy inbound links in an attempt to deceive Google for higher rankings.
In simpler terms, Google took punitive measures against sites that violated their rules and guidelines. Google has consistently viewed Search Engine Optimization (SEO) as a positive and constructive strategy for achieving favorable search visibility.
Google explicitly asserted that SEO is not synonymous with spam. However, the crucial distinction lies in the methodology employed—there exists a fine line between positive, constructive SEO and tactics that manipulate the system to achieve desired results. The implementation of the Penguin Update reinforced Google's commitment to maintaining the integrity of search results and penalizing practices that deviate from ethical SEO standards.
Hummingbird (2013): Emphasized understanding user intent and context in searches.
The Hummingbird update, announced on September 26, 2013, and already in operation for a month, signified a significant shift in Google's search algorithm. Named "Hummingbird" due to the speed and precision associated with hummingbirds, this update placed a heightened emphasis on natural language queries, prioritizing context and meaning over individual keywords.
TechCrunch characterized the advent of Hummingbird 1.0 as "the biggest overhaul to Google since the 2009 'Caffeine' overhaul," which had focused on speed and integrating social network results into search. Notably, Hummingbird impacted "around 90% of searches."
The crucial change introduced by Hummingbird was its ability to recognize complete-question searches, going beyond the traditional parsing of specific keywords.
This innovation empowered Google to accurately rank responses to long-tail question searches, marking a significant enhancement in its capacity to understand and cater to user queries in a more nuanced and context-aware manner.
Pigeon (2014): Focused on local search results and the ties between local and core algorithms.
On July 24th, 2014, Google introduced a new algorithm aimed at enhancing the relevance, accuracy, and usefulness of local search results, aligning them more closely with traditional web search ranking signals. The impact of these changes was evident in both Google Maps search results and general Google Web search results.
Dubbed the Pigeon update by the search community (coined by Search Engine Land following discussions with Danny Sullivan about an impending algorithm for local search), this update signaled a significant shift for businesses targeting local traffic.
In addition to prioritizing local search, businesses needed to consider search queries with a local intent.
This was particularly crucial in regions where local search results weren't explicitly displayed on Google's search results page. In such cases, maintaining a presence in organic search results became a valuable strategy for businesses seeking to maximize their visibility and reach.
Mobilegeddon (2015): Gave priority to mobile-friendly websites in mobile search results.
The mobile-friendly update, rolled out on April 21st, 2015, potentially provided a ranking boost to pages that were optimized for mobile devices in Google's mobile search results. Often referred to as Mobilegeddon by Search Engine Land, this update marked a pivotal moment in Google's algorithm.
In a clear announcement, Google specified that, commencing April 21st, 2015, they would be expanding the use of mobile-friendliness as a ranking signal.
This change was not confined to specific languages or regions; it had a global impact on mobile searches, promising a substantial influence on search results. As a result, users were expected to experience enhanced ease in obtaining relevant, high-quality search results that were specifically optimized for their mobile devices.
RankBrain (2015): Introduced machine learning for understanding search queries better.
RankBrain, introduced in the spring of 2015 and officially disclosed on October 26 of the same year, represents a system through which Google can enhance its understanding of the probable user intent behind a search query.
Google dubbed RankBrain as its machine-learning artificial intelligence system, a revelation made by Bloomberg and later confirmed to Search Engine Land by Google.
Although operational for several months before its announcement, RankBrain had remained under wraps.
RankBrain constitutes one of the myriad signals—numbering in the hundreds—that collectively shape the algorithm determining the appearance and ranking of results on a Google search page
Impressively, within a short span since its deployment, RankBrain had ascended to become the third-most significant signal influencing the outcome of a search query.
Possum (2016): Enhanced the importance of the user's location in search results.
Possum, a term coined by the local search community, refers to a substantial Local algorithm update that took place on September 1, 2016.
This moniker, proposed by Phil Rozek, carries a metaphorical significance as it aligns with the perception that numerous business owners believe their Google My Business listings have vanished, whereas, in reality, they have merely been filtered—they are essentially playing possum.
The primary objective behind the update was twofold: to broaden the diversity of local search results and to deter spam from achieving prominence in the rankings.
Fred (2017): Targeted low-value content that primarily existed for revenue generation.
Google's Fred algorithm update was implemented with the aim of eliminating what Google identified as low-quality results—specifically, websites that heavily depended on thin content and employed aggressive ad placement strategies.
Gary Illyes, a representative from Google, emphasized the continuous nature of algorithm updates and revealed that ongoing updates were playfully designated as Fred, unless specified otherwise.
The focal point of the Google Fred algorithm was to address black-hat SEO tactics geared towards aggressive monetization. The primary corrective action involved reducing the prominence of ads and enhancing the overall quality of the content.
Mobile-First Indexing (2018): Google started using the mobile version of a site for ranking and indexing.
On March 26th, 2018, Google announced that, following a year and a half of meticulous experimentation and testing, they had commenced the process of migrating websites adhering to the best practices for mobile-first indexing.
Traditionally, the Google index predominantly relied on the desktop version of a page’s content to assess its relevance to a user’s query. Given that a majority of users accessed Google through mobile devices, the index pivoted toward prioritizing the mobile version of a page’s content.
Google communicated the migration of websites to the mobile-first indexing process to webmasters and site owners through notifications in the Google Search Console. This shift aimed to align search results with the prevalent trend of mobile device usage.
Medic (2018): Primarily affected health and wellness sites, emphasizing expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (E-A-T).
The Google Medic update, also referred to as the August 1, 2018 Core Algorithm Update, marked a significant overhaul of the Google search algorithm on August 1, 2018.
A primary objective of the Google Medic update was to tackle the issue of "Your Money or Your Life" (YMYL) pages. YMYL pages encompass web pages with the potential to impact an individual's health, financial stability, or overall well-being. Examples of YMYL pages include those focused on financial products and services, medical and health information, and legal advice. The Google Medic update sought to enhance the quality and accuracy of YMYL pages, aiming to shield users from misinformation or potentially harmful content.
Renowned SEO influencer Barry Schwartz coined the term "Google Medic" for this algorithm update, noting that over 42 percent of the affected sites belonged to the medical, health, fitness, or healthy lifestyle categories.
The Medic update aimed to underscore and enhance the expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (E-A-T) of pages capable of influencing a person’s well-being. Google penalized pages with perceived low or no E-A-T while rewarding websites that demonstrated a high level of E-A-T. This shift aimed to uphold user safety and promote reliable content in critical areas impacting users’ lives.
BERT (2019): Leveraged natural language processing for better understanding context in search queries.
In 2018, Google introduced an open-source natural language processing (NLP) pre-training technique called Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, commonly known as BERT. This release empowered individuals worldwide to train their own cutting-edge question answering systems and various other models.
In October 2019, Google announced the integration of BERT into its production search algorithms in the United States.
It's important to note that BERT is not a direct algorithmic update impacting on-page, off-page, or technical factors. Instead, BERT is focused on enhancing the understanding and correlation of search queries for more accurate results.
Through the implementation of BERT, Google aims to enhance its understanding of one in ten searches in the United States in English, with plans to expand to more languages in the future.
The primary objective is to grasp the correlation of prepositions, such as 'to' and similar words in search queries, establishing a more accurate context to deliver relevant search results.
Core Updates (2019-present, on going): Regular broad updates focused on improving overall search quality.
These updates mark significant milestones in the evolution of Google's search algorithms, shaping the landscape of online search and influencing SEO strategies. Each update signifies Google's commitment to refining and optimizing its search engine to provide users with more accurate, relevant, and high-quality results.
November 16, 2023