The only constant (K) on the World Wide Web and the SEO world is change. SEO and the web are constantly evolving .Google’s constant endeavor for improving the quality of search results is a known fact. Google introduced the PageRank technology to deal with the keyword spam that was prevalent in the mid 2000. But this innovation brought with itself the link building spam as an off shoot.
It also recently came up with the Panda Update to control the content spam and improve the quality of search results further. But this focus on content has already started an exodus of content in all forms on the web. How Google is going to determine the grain from the chaff is going to be the next big challenge now.
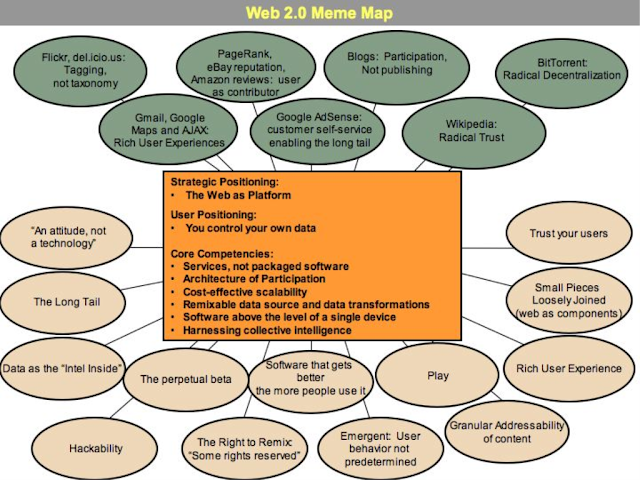
The following 4 quadrants explain the information and social connectivity very effectively.
Photo credit: http://www.novaspivack.com/
| created by Sebastian Faubel with Inkscape Vector Illustrator. (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
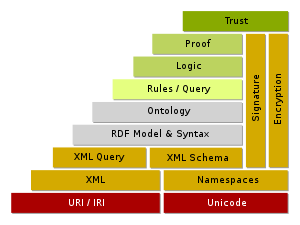
The next big evolution is the semantic search which is a much wider and deeper concept based on the science of semantics which has the potential to improve search accuracy by understanding searcher intent and the contextual meaning of terms as they appear in the web eco system or within a closed system like the search engine index, to generate more relevant results.
The Semantic Web is a set of technologies which are designed to enable a particular vision for the future of the Web – a future in which all knowledge exists on the Web in a format that software applications can understand and reason about. By making knowledge more accessible to software, software will essentially become able to understand knowledge, think about knowledge, and create new knowledge. In other words, software will be able to be more intelligent – not as intelligent as humans perhaps, but more intelligent than say, your word processor is today.
Semantics adds extra information to help you with the meaning of the information.
The Semantic Web does not only exist on Web pages.Web 3.0 works inside of applications and databases, not just on Web pages. Calling it a "Web" is a misnomer of sorts — it's not just about the Web, it's about all information, data and applications.
Data is the foundation on which such a web and search world can exist. Data in itself is meaningless but when data gets linked because of its relationships with various data sets available on the web, it becomes useful and meaningful and solves the purpose for which it was being searched as data becomes contextual due to the inter-connected relationships . The more it is connected the more powerful it becomes and gives more related information. Google Plus has that secret unlocked potential of correlating, connecting and linking all the data related to a profile and then integrating it with search with its data about people, places and pages.
Web 1.0 was about static pages linked together,
Web2.0 can be defined as the emergence of the web since the last boom of the .com’s (new web based sites/applications/technology- i.e.,Adsense, Wikipedia, Blogging), and the dynamic websites designed/programmed in terms of user interaction and web-based interaction .
The classic example of the Web 2.0 era is the “mash-up” — for example, connecting a rental-housing Web site with Google Maps to create a new, more useful service that automatically shows the location of each rental listing.
Web 3.0 works inside of applications and databases, not just on Web pages. Calling it a "Web" is a misnomer of sorts — it's not just about the Web, it's about all information, data and applications.
For such a semantic web, HTML5 which is a collection of features, technologies, and APIs brings the power of the desktop and the vibrancy of multimedia experience to the web and amplifies the web’s core strengths of user interaction and connectivity.
HTML5 includes the fifth revision of the HTML markup language, CSS3, and a series of JavaScript APIs. Together, these technologies enable you to create complex applications that previously could be created only for desktop platforms.
This is where Microdata comes in and it’s going to fundamentally change the way we discover and consume content on the web.
Microdata is a component of HTML5 aimed at adding more semantics and contextual information to existing content on a page. By doing so, Microdata provides others, like search engines or browsers, with more information about the contents of a page.
Microdata is an attempt to provide a simpler way of annotating HTML elements with machine readable tags than the similar approaches of using RDFa and Microformats.
Microdata vocabularies provide the semantics, or meaning of an Item. Web developers can design a custom vocabulary or use vocabularies available on the web. A collection of commonly used (and Google Supported) Microdata vocabularies located at http://data-vocabulary.org which include: Person, Event,Organization, Product, Review, Review-aggregate, Breadcrumb, Offer, Offer-aggregate. Other markup vocabularies are provided by Schema.org schemas. Major search engines rely on this markup to improve search results.Content expressed as microdata on the web page gets correlated easily to the data vocabulary it is giving information about making it easy for the search engine find relevance and connectivity.
Google has stated they only support a handful of these Microdata types which include: reviews, people, products, businesses and organizations, recipes, events, music, and video content. If your website has any of these types of content, you’re eligible for a Microdata implementation.
In one of our previous posts we have explained how to use the hCard microformat on http://blog.webpro.in/2010/05/what-is-hcard-integration.html and it can be seen clearly that if you express the contact address on the web page in an hCard format it becomes data having specified fields for street address, city, country, etc. which makes the content more co-related and meaningful.
The semantic web adds more meaning to the query for a search rather than just mapping words during the search process.
As an SEO I think it is high time we started incorporating microformats wherever possible . Some of the content which can be represented as microformats or as data are as follows:
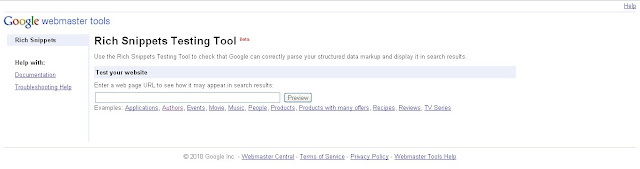
To check your markup, use the rich snippets testing tool.
More details about microformats on http://support.google.com/webmasters/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=146897
Panda or no Panda content has been king since the first web page was published on the web. It is Google who has become capable in picking quality content in 2012 and hence wants to reward sites with quality content with more visibility. But just adding content is not enough what has to be focused is how well the content is inter-connected to establish relevance.
More than the no. of inbound links it is important how well your web page gets inter-linked on the web as a whole. Sharing the links on social media and adding websites to Google web master tools and Bing web master tools help us achieve that purpose to a great extent but it is the representation of content in the form of data which ensures relationships and adds context will be the main task for an SEO in future.
The on-page SEO factors (used optimally, avoiding the over optimization) + The inter-linked connectivity of the aspects mentioned in the 4 quadrants above will determine the success of SEO campaigns in future.