What is structured data?
Structured data is highly-organized and formatted in a way so it's easily searchable in relational databases. We have to remember that not all data is created equal hence not all data is organized equally. This means the data generated from social media apps are completely different from the data generated by point-of-sales or supply chain systems.
Examples of structured data include names, dates, addresses, credit card numbers, stock information, geolocation, and more.
The most attractive feature of structured data is that one can easily input, search and update data and also correlate it more efficiently.
Google works hard to understand the content of a page. Clues on the page surely help Google in correlating content better. Since, structured data is a standardized and organized format for providing information about a page and understanding the page content; for example, on a product page, what is the name of the product, the price, availability, color, the image, description and so on.
Structured data schemas such as schema.org and data-vocabulary.org are used to define shared meaningful structures for markup-based applications on the Web. But, Google announced recently as schema.org is more popular and is widely being used so they will focus only on one SD scheme that is schema.org. From April 6, 2020 onwards, data-vocabulary.org markup will no longer be eligible for Google rich result features.
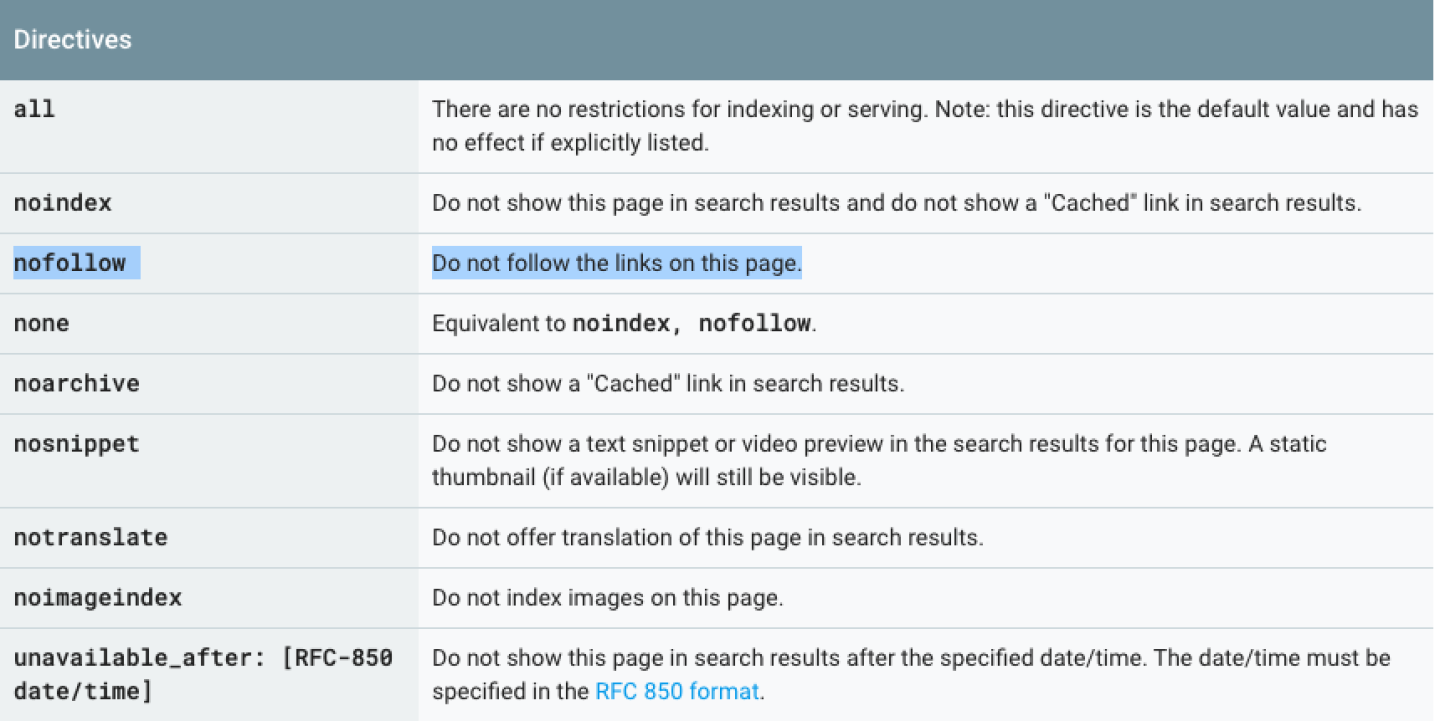
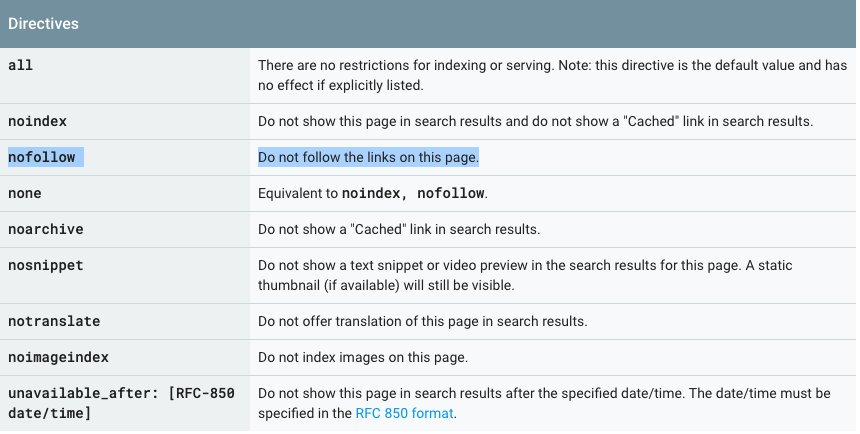
Is structured data a direct ranking factor?
Google Structured Data Guidelines clearly mentions the following:
Important:
Google does not guarantee that your structured data will show up in search results, even if your page is marked up correctly according to the Structured Data Testing Tool.
More so,
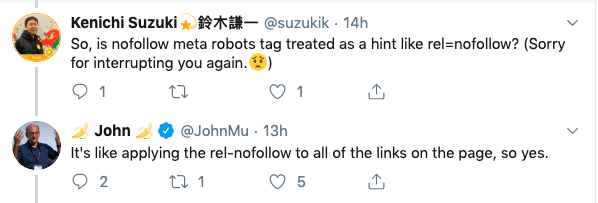
John Mueller of Google said on Twitter recently that although structured data, by itself, does not give you a ranking boost, it can help Google understand your content and thus help you rank in Google.
He added, in 2015 Google did say they may use structured data for ranking purposes. But just last year, Google said they don't want to depend on structured data for understanding the web, although they also said structured data is super important and here to stay.
There's no generic ranking boost for SD usage. That's the same as far as I remember. However, SD can make it easier to understand what the page is about, which can make it easier to show where it's relevant (improves targeting, maybe ranking for the right terms). (not new, imo)
— 🍌 John 🍌 (@JohnMu) April 2, 2018






 Google posted on the webmaster blog today that they have updated the review rich rules for how and when it shows the reviews rich results. Search results that are enhanced by review rich results can be extremely helpful when searching for products or services (the scores and/or “stars” you sometimes see alongside search results).
Google said that to make the review rich results more helpful and meaningful, they are now introducing algorithmic updates to reviews in rich results.
Google posted on the webmaster blog today that they have updated the review rich rules for how and when it shows the reviews rich results. Search results that are enhanced by review rich results can be extremely helpful when searching for products or services (the scores and/or “stars” you sometimes see alongside search results).
Google said that to make the review rich results more helpful and meaningful, they are now introducing algorithmic updates to reviews in rich results.
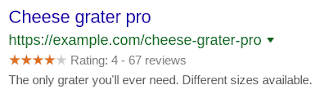 The main takeaway from this is that if the functionality of posting the reviews on the site is such that they can be moderated or updated then they will not be shown. This applies to even the reviews posted via the third party widgets.
The main takeaway from this is that if the functionality of posting the reviews on the site is such that they can be moderated or updated then they will not be shown. This applies to even the reviews posted via the third party widgets.